You are here
01 - Assess & engage
SEE ALL
CHAPTERS
Assess & engage
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
Diagnosis can be set after a thorough clinical examination and confirmed by imaging. Clinical findings with patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis can include complaints of restricted knee function, pain increase with activity, stiffness (especially morning stiffness), decreased range of movement, and knee swelling. Other symptoms may include crepitus and pain and stiffening occurring after prolonged resting. The condition negatively affects mental health and overall quality of life.
Pain characteristics and chronicity can suggest the stage of knee osteoarthritis:
Stage 1: pain is sharp and occasional but does not affect daily activities significantly
Stage 2: pain becomes constant, affecting daily activities; stiffness starts to occur
Stage 3: constant, dull pain with unpredictable episodes of exacerbation; daily activities are seriously affected
What should you be looking for to diagnose knee osteoarthritis?
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis is largely based on clinical examination. When examining the affected limb, look for the following:
- Tenderness around the joint line
- Reduced range of motion
- Joint deformity and swelling
- Instability (when weight bearing).
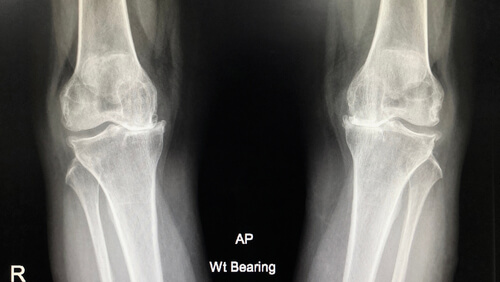
Imaging for knee osteoarthritis
X-ray is the reference to confirm the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis and grade its severity. Ultrasound and MRI may also be used.
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis can include both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical methods such as the Guided DolorClast® Therapy. When choosing appropriate treatment, you should consider the patient’s comorbidities, including CVDs (cardiovascular diseases), gastrointestinal bleeding risk, and renal capacity.
A holistic approach is crucial, as only by taking into account all factors is it possible to obtain satisfactory and long-lasting outcomes. Talking to your patient about their awareness of the disease and resolving any doubts makes them more inclined to follow the complete treatment regimen and ensure satisfactory treatment results.
What causes pain in the course of knee osteoarthritis?
Pain can have multiple origins, such as mechanical strain, degeneration of tissues, inflammation, and edema. The tendency is often to treat the dominating symptom, in this case, pain but not its cause. With quick fixes such as painkillers, the underlying inflammation can be neglected. Although the patient may be satisfied with the disappearance of the pain, it may cause more damage due to the stress applied to the silenced injury. Therefore, you need a treatment method to tackle the underlying cause of pain. For example, Radial Shock Wave Therapy, compared to other approaches, effectively reduces pain and inflammation with no side effects.